A new model for risk adjustment
As healthcare continues to rapidly evolve, the Medicare Advantage risk adjustment model must also adapt to ensure accurate risk adjustment. This article discusses the proposed changes from Risk Adjustment Model V24 to V28, outlined in the Medicare Advantage 2024 Advance Notice. The new model introduces a more refined risk adjustment framework, reflecting CMS' focus on accurately identifying and auditing risk-adjustable conditions that align with patients' care, ultimately impacting reimbursement claims for Medicare Advantage Organizations (MAOs). This model change, coupled with the RADV final rule, underscores the importance of precise risk adjustment in the Medicare Advantage program.
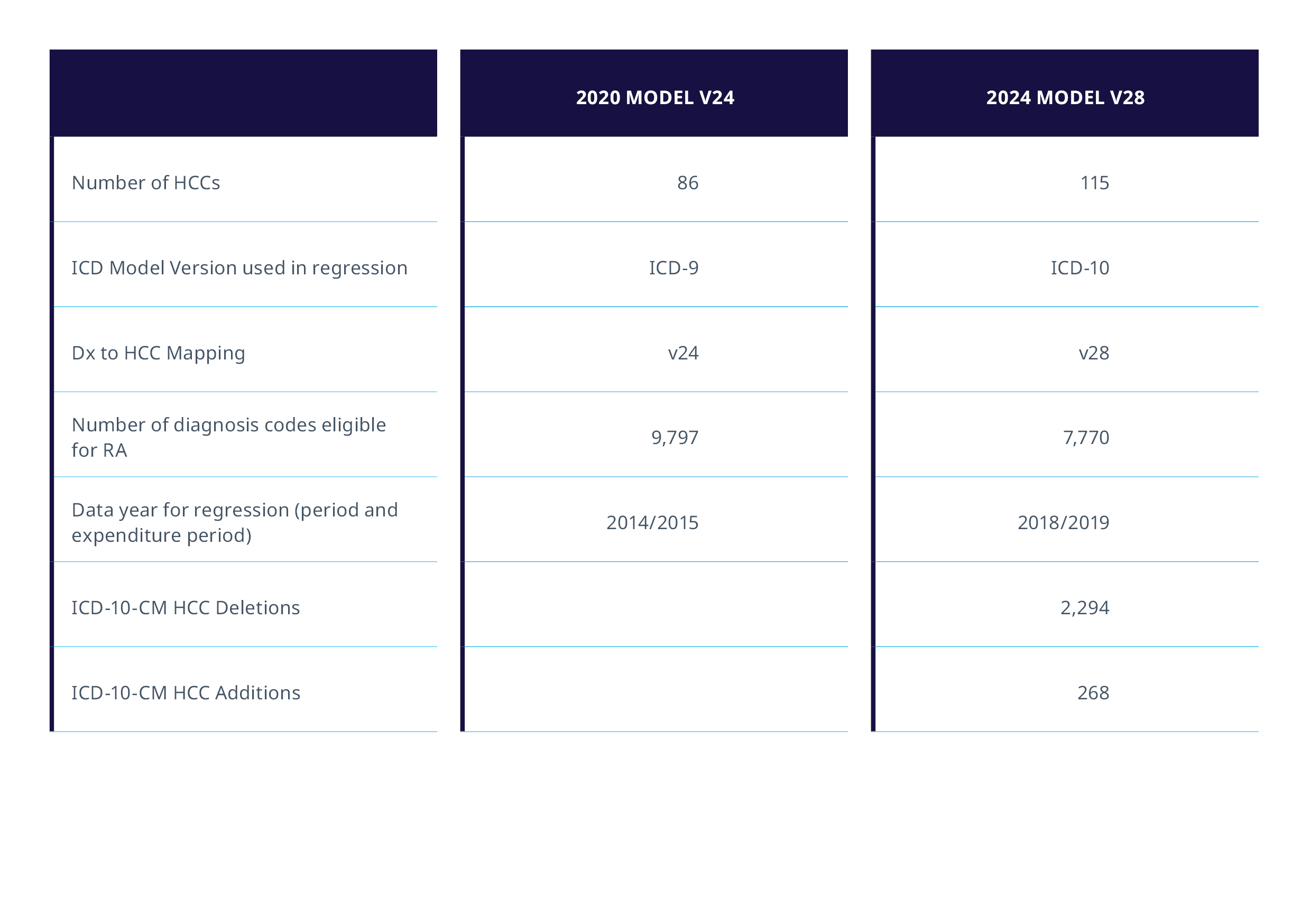
V28 model refinement and changes (Table 1):
- Increased number of HCCs from 86 to 115
- Changes to ICD-10-CM to HCC mapping
- Changes in coefficient values
- Removal and addition of diagnosis codes
What changes are being made?
The model refinements stem from a recalibration using 2018/2019 data, aligning with recent utilization, coding, and expenditure trends. A significant change with this transition removes 2,294 ICD-10-CM codes previously linked to HCCs in V24 which no longer correlate with V28. CMS has acknowledged that while these changes may affect a patient's risk score, they decided to remove codes that raised cost predictability concerns, had small coefficients, were rare, or had specificity issues, thus constructing a more precise risk adjustment framework. The elimination of risk-adjustable clinical codes will result in the removal of specific disease coefficients, potentially affecting a patient's RAF score. For instance, in Example 1, the omission of Protein Calorie malnutrition (0.455) illustrates this impact. Notably, certain coefficients, such as Type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications (E11.9), have been adjusted, likely leading to reduced RAF scores for patients with diabetes-related conditions. The financial impact on MAOs will hinge on case mix variations.
The following example demonstrates the potential impact on RAF scores based on the disease coefficients:
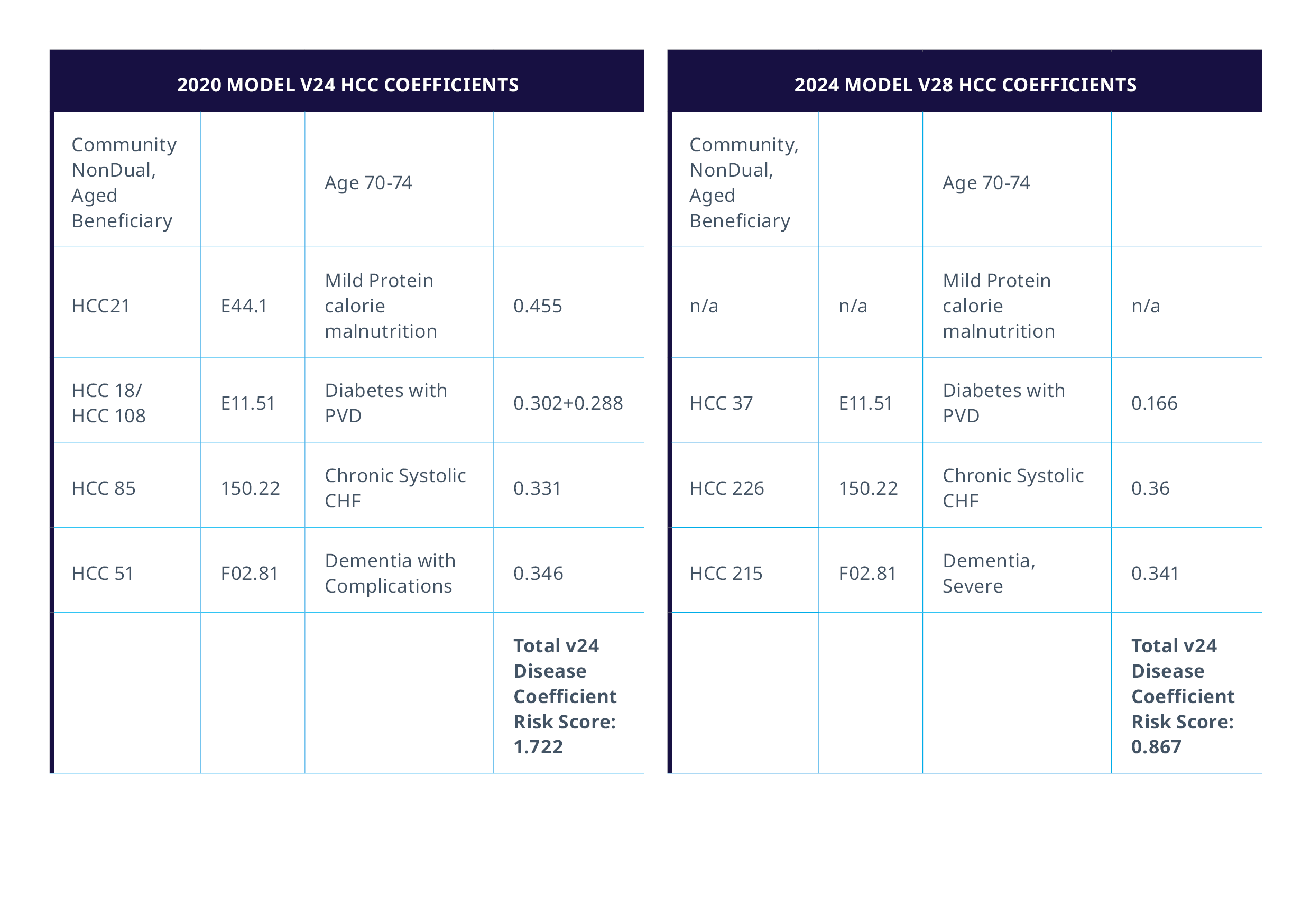
Example 1: Significant negative impact on the risk score based on disease coefficients in a Community, NonDual, Aged 71-year-old female beneficiary
The transition has added an additional 268 diagnosis codes that were not previously linked to a payment HCC but will now be linked to a payment HCC. Of the 268 new ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes, 95 belong to the "Certain Conditions originating in the perinatal period" chapter. Figure 3 also displays 17 new codes from the "Congenital malformations, deformations, and Chromosomal abnormalities" chapter. This means that over 40% of the new codes that map to a payment HCC in the V28 model represent conditions that are not commonly encountered in most patients in the Medicare Advantage population.
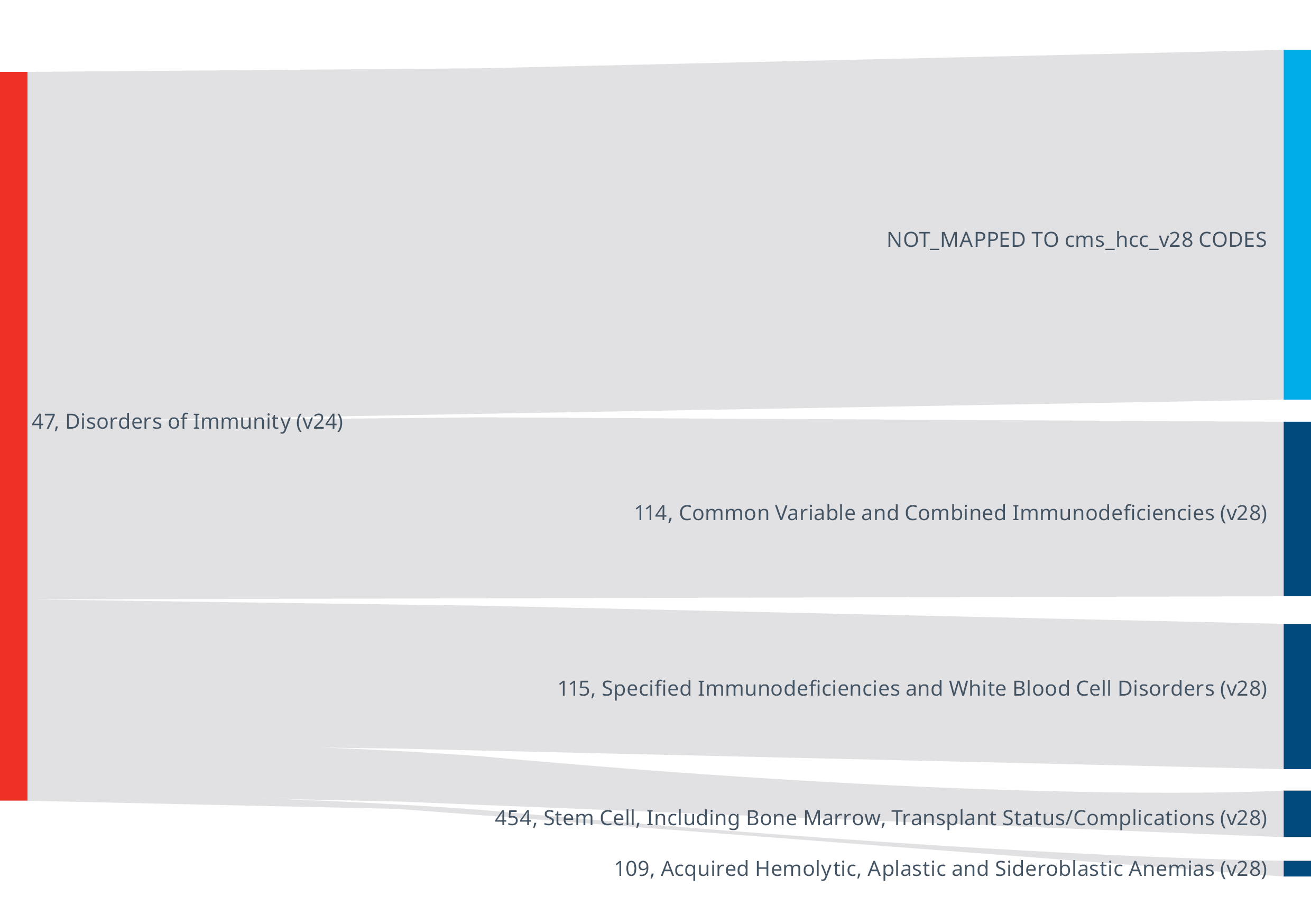
The transition from V24 to V28 in the Medicare Advantage risk adjustment model carries significant implications for both RAF scores and financial outcomes. This shift is projected to result in a notable -3.12% impact on MA risk scores by CY 2025, leading to substantial net savings of $11.0 billion to the Medicare Trust fund in 2024, according to CMS. Alongside this, the new RADV final rule emphasizes the critical importance of accurately identifying HCCs to determine RAF scores and, consequently, reimbursement. With alterations in coefficients and the removal of certain conditions, precise HCCs identification and robust supporting evidence retrieval from unstructured medical records have become paramount.
IQVIA, committed to empowering both payers and providers, harnesses advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning technologies. This innovative approach enables our solutions to adapt to shifting regulatory frameworks. NLP efficiently identifies relevant codes and supporting evidence, ensuring an impressive 97% HCC coding accuracy rate. This expedites chart review processes, optimizes resource allocation, and establishes collaborative quality assurance workflows to effectively manage your risk adjustment program. Is your organisation ready for this transition?
Related solutions
Insights are trapped in mountains of text. NLP sets them free.
IQVIA is using vast quantities of data in powerful new ways. See how we can help you tap into information from past trials, patient reported outcomes and other sources to accelerate your research.
Drive better care and greater efficiency through deep, actionable insights.